- Step
-
-
-
Registering at business.gov.au
Business names or company names aren't types of IP. You can register your business name at business.gov.au
Trade marking your business name
Business name registration doesn't stop others from using the same business name. If you'd like to do this, you should consider registering your business name as a trade mark.
Registering at business.gov.au
Business names or company names are not types of IP. You can register your company name at business.gov.au.
If you wish to trade using a name other than your registered company name, you should consider registering that trading name as a business name. You can also do this at business.gov.au
Trade marking your company name
Company name registration doesn't stop others from using the same company name. If you'd like to do this, you should consider registering your company name as a trade mark.
Trade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleLicensing a domain name
A domain name isn't a form of IP, so having a trade mark application or registration doesn't automatically entitle you to the domain name license.
Licensing of domain names is carried out by companies on behalf of .au Domain Administration (auDA) on a first in, first served basis.
auDA only administers the .au country code - it doesn't extend to other countries, nor generic top-level domains such as .com or .org regulated by other bodies.
In certain circumstances you can register a domain name as a trade mark if it meets the requirements of the Trade Mark Act 1995. The rules and policies for registration of domain names in com.au may be viewed at auDA.
Visit auDATrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleCopyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightOther considerations
Trade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightPatents
A patent legally protects your invention or how something works. You can use a patent for new technology, devices, substances or processes.
Examples of patents
Learn about patents Google Maps
Google Maps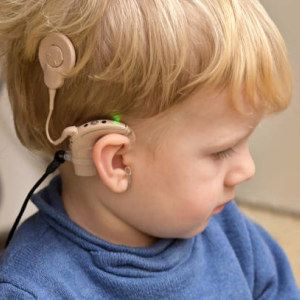 Cochlear implant (bionic ear)
Cochlear implant (bionic ear) Polymer (plastic) bank notes
Polymer (plastic) bank notesTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightPatents
A patent legally protects your invention or how something works. You can use a patent for new technology, devices, substances or processes.
Examples of patents
Learn about patents Google Maps
Google Maps Cochlear implant (bionic ear)
Cochlear implant (bionic ear) Polymer (plastic) bank notes
Polymer (plastic) bank notesPatents
A patent legally protects your invention or how something works. You can use a patent for new technology, devices, substances or processes.
Examples of patents
Learn about patents Google Maps
Google Maps Cochlear implant (bionic ear)
Cochlear implant (bionic ear) Polymer (plastic) bank notes
Polymer (plastic) bank notesDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightPatents
A patent legally protects your invention or how something works. You can use a patent for new technology, devices, substances or processes.
Examples of patents
Learn about patents Google Maps
Google Maps Cochlear implant (bionic ear)
Cochlear implant (bionic ear) Polymer (plastic) bank notes
Polymer (plastic) bank notesCopyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightDesign rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightCopyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightOther considerations
Design rights
A design right legally protects the overall appearance of your new and distinctive product. The appearance may be a combination of shape, colour, configuration pattern and ornamentation.
You can use a design right for the look of a whole, physical product if you're producing it on a commercial scale.
Examples of design rights
Learn about design rights Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofa
Zimmerman dressAudi car modelKing Furniture sofaTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. There are some things that can't be protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these.
A sound trade mark protects a distinguishing auditory piece. It could be a jingle, sung or spoken words, or even a mechanical clicking noise.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottleOther considerations
Copyright
Copyright protection is free and automatic. It protects your original expression of an idea as soon as you document it.
Copyright protects art, non-commercial design, music, literature or film. For example, the Game of Thrones TV series is protected by copyright.
The Attorney-General's Department manages copyright in Australia.
Learn about copyrightTrade marks
A trade mark legally protects your brand, and helps customers distinguish your goods and services from competitors.
You can use a trademark for a logo, word, phrase, letter, number, sound, scent, picture, movement, aspect of packaging, or any combination of these. You'll need to pick a name for your new plant variety that hasn't already been protected with a trade mark.
Examples of trade marks
Learn about trade marks Nike swoosh logo
Nike swoosh logo Cadbury purple
Cadbury purple Shape of a Coca-Cola bottle
Shape of a Coca-Cola bottlePlant Breeder's rights
A plant breeder's right (PBR) legally protects the new plant variety you have developed.
You can use a PBR for new variations of plants and trees including flowers, vegetables, fruits, bushes and shrubs.
Examples of PBRs
Learn about plant breeder's rights Barley Spartacus CL
Barley Spartacus CL Apple Bravo Apple
Apple Bravo Apple Flower Flame Legacy
Flower Flame LegacyPlant Breeder's rights
A plant breeder's right (PBR) legally protects the new plant variety you have developed.
You can use a PBR for new variations of plants and trees including flowers, vegetables, fruits, bushes and shrubs.
Examples of PBRs
Learn about plant breeder's rights Barley Spartacus CL
Barley Spartacus CL Apple Bravo Apple
Apple Bravo Apple Flower Flame Legacy
Flower Flame LegacyPlease note this guide is intended as general advice only. For specific assistance or advice, we recommend that you contact an IP professional.
Related content
Types of IP
There are four types of IP you can register through IP Australia.
Case studies
Here's how Australian businesses are working with the intellectual property system to protect and commercialise their ideas.
IP in everyday life
You may not notice, but you interact with products protected by intellectual property (IP) every day.



